Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) refers to investments made by individualities or companies from one country into business gambles in another. This investment generally involves establishing new enterprises, expanding being businesses, or acquiring power stakes in foreign companies. FDI plays a pivotal part in global profitable growth and request integration.
FDI is described as investment by a company or an individual of one country into business interests in another country. Usually, this investment involves gaining new business ventures, growing current businesses, or gaining ownership in overseas enterprises.
It may come in many forms, which include wholly owned subsidiaries, joint ventures, and mergers and acquisitions. Due to energetic management and sustained engagement, FDI is unique from portfolio investment. The government frequently supports foreign direct investment to enhance economic growth and generate more jobs.
FDI is divided into two categories, which are:
- Inward FDI
- Outward FDI
Inward FDI is those that involve foreign investors investing in the domestic economy of the country, and outward FDI is those that involve home enterprises expanding overseas or abroad. These investments play an important role in global unification and foster economic interlinkage between countries. Conversely, investors should also consider the regularity issues and political volatility before investing.
For developing nations that may not have access to domestic capital markets, foreign direct investment (FDI) serves as a vital source of foreign capital. FDI is a necessary driver for many countries, such as India, the United States, the United Kingdom, and the United Arab Emirates. In India, FDI flows into many sectors, including information technology, retail, and telecommunications. The UAE evaluates investments in real estate, finance, and tourism. In the USA, the investments are drawn to industries like real estate, technology, and energy. While the UK sees investments in sectors like pharmaceuticals, financial services, and manufacturing.
FDI has several impacts. Excessive dependence on foreign investment may increase economic vulnerability although it can stimulate economic growth and employment creation. Moreover, if FDI is not managed properly, it can cause disparity of income and exploitation of local resources. However, strategic use of foreign direct investment (FDI) may substantially improve global marketability and improve a nation’s economic standing.
The major part of Pakistan’s economic development relies on foreign direct investment (FDI); technology, money, and experience are provided by it. In the financial year 2024, FDI climbed 17% to $1.9 billion from $1.62 billion the year before.
Hong Kong elevated their stake to $358.5 million from $250 million. China continues to be the biggest financier in FY2024 with $568 million, down from $692 million in FY2023. Furthermore, the United States ($137 million), the United Kingdom ($268 million), and Singapore ($100 million) are the other renowned investors.
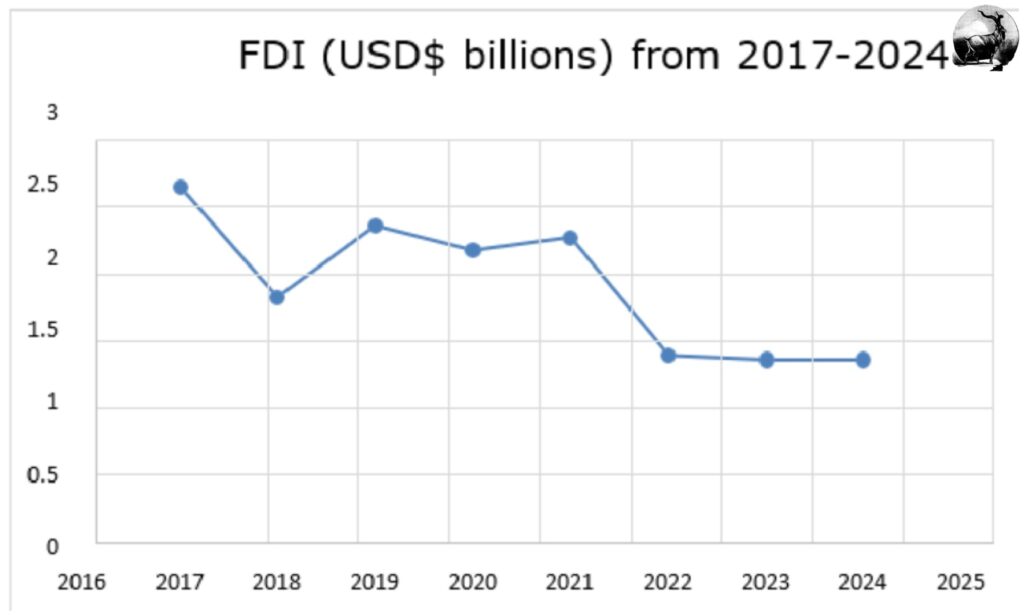
In the first quarter of financial year 2025, FDI increased from $520 million to 48%, $771 million. China made a substantial contribution by contributing 52% or $404 million of the entirely foreign direct investment acquired this quarter.
In FY2024, with $799.9 million, a slight amount from $898.5 million in FY2023, the largest amount continues to be received by the electricity industry. In the previous year, the oil and gas exploration industry increased to $303.6 million from $137 million. However, in the financial sector, the investment decreased to $208 million, unlike $276 million in the previous financial year.
The Pakistani government developed the Special Investment Facilitation Council (SIFC) to promote foreign direct investment boost. By serving as a “single window” for stakeholders and endorsing collaboration between government agencies. This organization aims to accelerate investment procedures and illustrate foreign investment.
Ultimately, the United States, the United Kingdom, Singapore, and Hong Kong all make significant investments in Pakistan, although China remains to be the country’s top supplier of FDI. This investment’s primary recipients are the oil, gas, and power industries, which shows the country’s key emphasis on developing an energy framework.
Investments are extended across a number of sectors in Pakistan, all of which contribute to the nation’s profitable growth and progress.
Stock Market A main point for fiscal commitments, the Pakistan Stock Exchange (PSX) draws both original and foreign investment. Organizations use stock immolation to produce capital in colorful disciplines, similar as finance, energy, and manufacturing.
Construction Because of structure and metropolitan development, the construction sector receives a lot of investment. The construction sedulity is told by real estate formulators and massive systems like the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC).
Information Technology (IT) The IT assiduity is raising finances for startups and software development and growing fleetly. For both domestic and overseas investors, because of government prices and expert training, it is a desirable assiduity.
Manufacturing CPEC’s Special Economic Zones (SEZs) plump foreign direct investment (FDI) and artificial development. Pakistan’s frugality explosively relies on investments in manufacturing, specifically in the disciplines of fabrics, motors, and pharmaceuticals.
Collectively these industries impact Pakistan’s economic environment and present an array of chances for investors aiming to broaden and make money.
Pakistan has seen a positive trend lately in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). FDI grown by 17% to $1.9 billion, up from $1.62 billion to $1.9 billion the prior year. In the initial quarter of fiscal year 2025 this development continued with a totaling $771 million,48% rise to $520 million in the identical time frame last year. China remains top investor, providing $568 million in fiscal year 2024 and $404 million in the initial quarter of fiscal year 2025. Utmost of the capital was drawn by the power sector, acquiring$ 800 million in financial time 2024. These advancements demonstrate expanding investor confidence in Pakistan’s economic policies and investment climate.


